本文主要探讨GPT插件的精妙运用,助你轻松掌握这一强大工具,让你的聊天体验更上一层楼。
一、运行原理
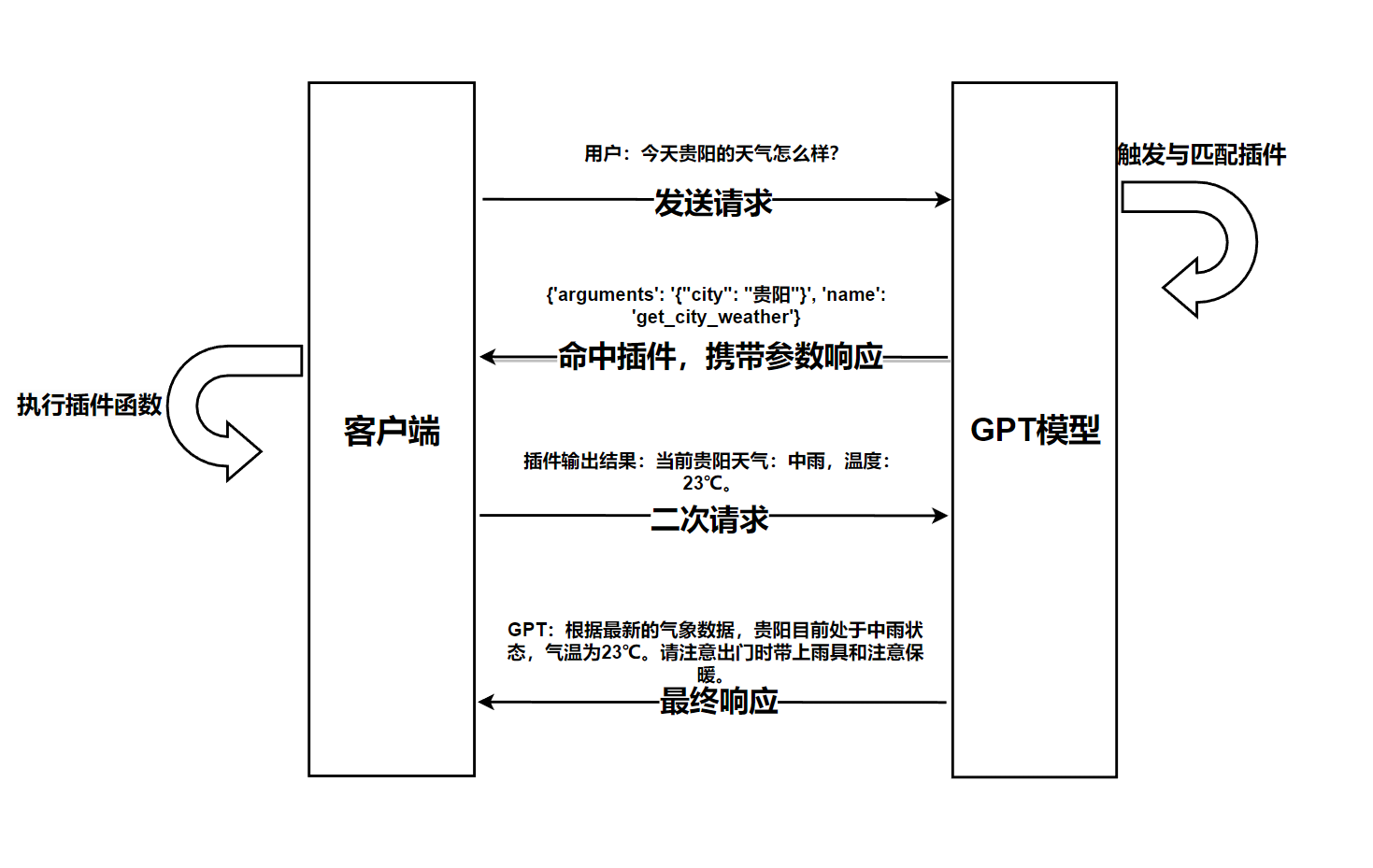
首先我们在客户端发起一个聊天会话,比如询问GPT:“今天贵阳的天气怎么样?”,同时为了使用我们自己的插件,我们还需要告诉GPT有哪些插件可用,目前这需要我们在发起聊天时传递一个支持的插件列表给GPT。
然后GPT收到我们的聊天后,它会根据用户的聊天内容去匹配插件,并在返回的消息中指示命中了哪些插件,这个匹配是根据GPT的语言理解能力做出的。
然后客户端就可以检查命中了哪些插件,并调用执行本地相应的插件方法。插件方法是在本地执行的,这也比较合理,如果放到GPT服务端,GPT不仅要适配各种计算能力,还可能面临巨大的安全风险。
然后客户端将插件的执行结果附加到本次聊天会话中,再次发起聊天请求,GPT收到后,会根据首次聊天请求和插件生成的内容组织本次聊天响应结果,再返回给用户。
这样就完成了一次基于插件的GPT会话。
二、插件开发
1、开发插件,设置好插件调用函数,比如:开发获取天气的函数:get_city_weather,示例代码
# 获取城市天气
def get_weather(city_name):
params = {
"key": "xxxxxx", # 高德地图天气API:https://lbs.amap.com/
"city": city_name,
}
try:
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo?parameters"
r = requests.get(url, params=params)
data = r.json()
except:
data = {"error": "API请求失败,无法获取到天气数据。"}
return str(data)2、我们写好自己的工具之后,需要定义一个为GPT看懂的格式(其实就是一个Json对象),Json对象说明:
# 天气查询插件,示例
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取`city_name`的当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city_name": {
"type": "str",
"description": "要查询的城市名称,例如:北京、上海",
}
},
"required": ["city_name"],
},
},
}
]三、最终的代码示例
"""
简单的插件开发示例
"""
import json
import requests
from loguru import logger
from openai import OpenAI
# 这个使用智谱的API,需要先在智谱官网注册账号,然后获取API Key:https://maas.aminer.cn/
client = OpenAI(
base_url="https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/",
api_key="xxxxxx",
)
# 定义天气插件JSON
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取`city_name`的当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city_name": {
"type": "str",
"description": "要查询的城市名称,例如:北京、上海",
}
},
"required": ["city_name"],
},
},
}
]
# 天气查询插件函数
def get_weather(city_name):
"""获取`city_name`的当前天气"""
params = {
"key": "XXXX",
"city": city_name,
}
try:
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo?parameters"
r = requests.get(url, params=params)
data = r.json()
except:
data = {"error": "API请求失败,无法获取到天气数据。"}
return str(data)
# 聊天上下文,初始为空
messages = []
# 我的三个问题
query_list = ["请问现在贵州的天气怎么样?"]
print("<---气插件演示示例--->")
# 遍历询问我的问题
for query in query_list:
params = dict(
model="GLM-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": query}],
stream=False, # 这里演示只用False,这个参数控制是否流式返回结果
)
if tools:
params["tools"] = tools
params["tool_choice"] = "auto"
# 请求GPT,并拿到响应数据
response = client.chat.completions.create(**params)
print("靓仔: ", query)
# 判断是否调用了插件
if response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
# 获取调用的函数信息
function_call = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function
logger.info(f"Function Call Response: {function_call.model_dump()}")
function_name = function_call.name # 插件函数名称
function_args = json.loads(function_call.arguments) # 插件函数参数
# 【注】多个插件时,这里需要进行判断调用哪个插件函数,这里直接调用插件了,不进行其他判断了
tool_response = get_weather(function_args["city_name"])
logger.info(f"Tool Call Response: {tool_response}")
# GPT的原始回答添加到聊天上下文中
params["messages"].append(response.choices[0].message)
# 将插件的响应结果添加到聊天上下文中
params["messages"].append(
{
"role": "tool",
"content": tool_response, # 调用函数返回结果
"tool_call_id": response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].id,
}
)
# 获取到插件运行的结果之后,再次请求GPT,并拿到最终的响应数据
second_chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(**params)
output = second_chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
print("GLM: ", output)
else:
output = response.choices[0].message.content
print("GLM: ", output)

暂无评论